Introduction
Economic is something that is related to production and consumption of the goods and services by the consumer. It provides data that the company is fulfilling demand of the market. It is required for the business to make the consumption according to the demand of the consumer so that they can be satisfied. Economic is divided into two parts as microeconomic and macro economic. It provides the data of the consumption that the consumers are consuming. It helps to analysis at economic level that the consumption of any goods is sufficient or it is out of limit so that it can be controlled (Wilhite and Fong, 2012).
Assignment Prime is an online assignment writing service provider which caters the academic need of students.
Get Best Pricing Quotes Free Samples Email : help@assignmentprime.com Order NowAt present situation, economic analysis helped to analyse the present situation of consumption of antibiotics. It helped to take measure to reduce the consumption of antibiotics.
Issues related to over consumption of antibiotics
Antibiotic is also known as antibacterials. It is a kind of drug. It is a drug that is used to prevent the bacterial infection in the body. It is used to kill the bacteria and also helps to control the growth of the bacteria.
Impact of over consumption of antibiotics
Fatal Diarrhea: Antibiotic causes many problem to the children. There are many antibiotic that are suggested when a child suffers from common cold. It helps to eliminate such disease but cause side effects to the body of the patient (Schoorman, Mayer and Davis, 2016).
Good bacteria to bad one: Antibiotic is used to kill the germs and bacteria in the body. But there are few bacteria in the body that are necessary but antibiotic kills and stop the growth of those bacteria also.
Untreatable Gonorrhea: Antibiotic causes untreatable diseases in the body. These factors causes pain and also causes provocative disease, eye infection, tubal infertility.
Economic Cost
As per the study of Centers for Disease control and prevention, Antibiotic increases direct healthcare cost and also increases cost due to mislaid productivity. When an individual consume antibiotic then it causes many diseases in the body that increases the cost burden.
Global death
Excessive use of the antibiotic finally resulted into the death. It causes many diseases in the body. It also affects the important organs of the body and it hinders them to perform well and after the time result in death.
Sources of antibiotics are as follows
- Medicine- Medicine is the biggest source of antibiotics. Antibiotics are used to kill the germs and bacteria in the body (Pohl, 2017). Doctors are suggested antibiotics even for the common cold and influenza. In medicine antibiotics are used to kill the germs and bacteria so that disease can be treated as soon as possible.
- Agriculture- There are many medicines that are used in agriculture field to kill the insects. When these medicines are used on the crops and finally consumed by the human then it causes disease to the body. Antibiotics are moved to the body due to the agriculture activities.
- Pharmaceutical processing plants dumping drugs into waste water.
Worst over consumer:
- The excessive use of the antibiotics resulted in death of the user.
- It creates many diseases into the body of the consumer.
- When it is used in agricultural activities and when it is consumed by the animals as their feed then it creates problem to their body and it also affects the productivity.
- Excessive use of antibiotics in agricultural activity damage the crops also.
- It affects the livestock animals badly (Kolstad, 2011).
- When it is used then it goes inside the earth and make the ground water dirty and polluted.
Economic theory to the over consumption
Following are the economic theory that explain the over consumption of antibiotics as:
Relative income theory of consumption:
As per the income theory, it is considered that the antibiotics that are used in medicines are more effective to treat the disease. It is required to adopt to provide the best treatment that is beneficially for the patient. It is cost effective and consumer can easily use this. Income theory says that the production must be made as per the income of the consumer so that they can consume it. It is important to produce the medicine that can be easily afforded by the consumer.
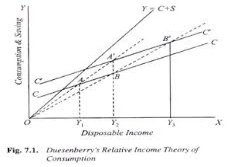
It is also required because the medicines that are available for the treatment are very costly and it can not afforded by the consumer. Antibiotics make the medicine more effective and it helps to treat the patient as soon as possible (Kalaitzidakis, Mamuneas and Stengos, 2011). It is not much costly. This theory says that the production must be according to the capacity of the consumer so that they can afford it.
Life cycle theory of consumption:
In this theory, it is assumed that the consumer will consume the goods and services if the cost of the goods and services allow. Consumer plan the services according to the consumption expenditure. It is assumed that the consumer may slightly increase the consumption if the expenditure increases (Kohler, Karlson and Holm, 2011).
_5c6cecc71ee30.jpg)
In the life time, consumer consumes that goods and services less than the income and finally earns more positive savings. The saving is invested by the consumer in number of things as assets, social standards. When someone face the issue related to the disease then firstly consider the expenditure that will be incurred in the treatment. If the expenditure is beyond the capacity then such person do not want to go for the treatment (Hoepner and et. al., 2012). Antibiotics that are used in the medicines provides help to the patient because these are more effective and less costly. On the other hand it creates many disease in the body but for a time it reduce the effects of the such diseases.
Permanent income theory of consumption:
As per this theory, it is assumed that the consumer make the consumption according to their long term income. People plan their consumption according to their permanent income. It is predicted when the expenditure on the consumption is very high then people prefer to take the services according to their permanent income. When it comes under diseases then when a patient has saviour disease then they take the treatment according to their permanent income. Antibiotics plays very effective role in this segment, it provides help to the patient to take the treatment which is not so costly but causes many diseases as well (Kelly and Bruestle, 2011).
_5c6ced10b8814.jpg)
Policies to reduce the consumption of antibiotics
There arr many things that can be used in place of the antibiotics and it is very helpful to reduces the effects of antibiotics (Fortin, Lemieux and Firpo, 2011). Antibiotics causes many diseases to the body and it kills the important bacteria that are present in the body. It is very important to adopt the alternative way to reduce the consumption of antibiotics.
Following are the policies that can be used to reduce the consumption of antibiotics as-
Use the natural alternatives
It is very important way that can be used to avoid the excessive use of antibiotics. It is required to use the natural sources for the treatment so that they can not affects the body adversely (Becker, 2010). There are many natural herbs available that can be used in treatment and these herbs effectively treat the disease and eliminate the chances for the future time. Like:
- Olive leaves- This is the best treatment that is used in fever, malaria, cold. This reduces the effects that occurs due to the excessive use of the medicines. Generally doctors suggested more antibiotics to the patient in case of cold. But it is the good natural thing that can be used in treatments.
Homeopathic Remedies
There is one homeopathic treatment i.e. Oscillococcinum. This treatment is available for the treatment of flu. It has very long effects that reduce the future disease. There are many homeopathic treatments are available that are more effective to treat the patient (Aoki, 2013). It is said that these treatments are very important and it eliminates the disease from the body for the permanent time.
Ayurvedic treatment
It is the good treatment that can be used in may disease. This treatment is not much effective instantly but when patient take the treatment for long time then it eliminate the disease permanently. It is not much costly and every one can easily afford it. In this treatment, natural things are used to treat the disease.
Conclusion
As per the above study it can be concluded that the excessive use of antibiotics are hazardous to the body. It is required to adopt the alternative ways to treat the disease so that it can not ham to the body. There are many alternative that can be used to eliminate the disease from the body as use of natural things, homeopathic treatment etc. these are the beneficial treatment and cost effective. Excessive use of antibiotics not only affects the human but also to the animals. There are many sources of antibiotics as medicines and agriculture. It is required to eliminate such factors so that it can not cause harm to the body.
Reference
- Aoki, M., 2013. Monitoring characteristics of the main bank system: An analytical and development view. Chapters, pp.342-374.
- Becker, G.S., 2010. The economics of discrimination. University of Chicago press.
- Fortin, N., Lemieux, T and Firpo, S., 2011. Decomposition methods in economics. Handbook of labor economics. 4. pp.1-102.
- Hoepner, A.G and et. al., 2012. Environmental and ecological economics in the 21st century: An age adjusted citation analysis of the influential articles, journals, authors and institutions. Ecological Economics. 77. pp.193-206.
- Kalaitzidakis, P., Mamuneas, T.P and Stengos, T., 2011. An updated ranking of academic journals in economics. Canadian Journal of Economics/Revue canadienne d'économique. 44(4). pp.1525-1538.
- Kelly, M.A and Bruestle, S., 2011. Trend of subjects published in economics journals 1969–2007. Economic Inquiry. 49(3). pp.658-673.
- Kohler, U., Karlson, K.B and Holm, A., 2011. Comparing coefficients of nested nonlinear probability models. Stata Journal. 11(3). pp.420-438.
- Kolstad, C., 2011. Intermediate Environmental Economics: International Edition. OUP Catalogue.